Encoding
The encoding layer defines the mapping between the document layer, and its byte string encoding.
Core API defines a canonical encoding scheme called Core JSON. Other encodings are also supported.
Core JSON
An implementation for Core JSON is built-in to the Python client library: core-api/python-client
Core JSON is a format that can be used to represent either Schema responses or Hypermedia response. It is designed to map cleanly to the Core API document model.
A document is represented using the JSON encoding. In addition to the standard set of JSON primitives, Core JSON adds the following:
- Document.
{"_type": "document", ...} - Link.
{"_type": "link", ...} - Error.
{"_type": "error", ...}
The top level element in a Core JSON response MUST either be a Document or an Error.
The media type for this scheme is: application/vnd.coreapi+json.
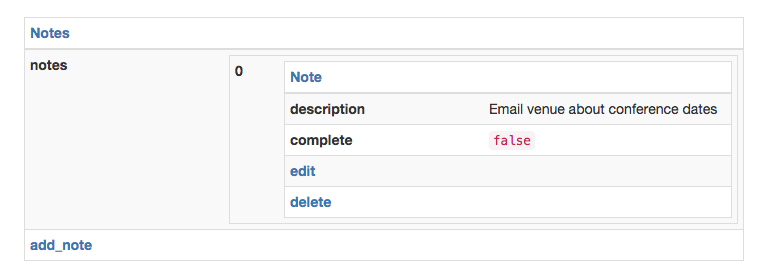
An example Core JSON encoded document is demonstrated below.
{
"_type": "document",
"_meta": {
"url": "/",
"title": "Notes"
},
"notes": [
{
"_type": "document",
"_meta": {
"url": "/1de153fe-6747-41d3-bc0e-d9d7d87e448a",
"title": "Note"
},
"complete": false,
"description": "Email venue about conference dates",
"delete": {
"_type": "link",
"action": "delete"
},
"edit": {
"_type": "link",
"action": "put",
"fields": [
{
"name": "description"
}, {
"name": "complete"
}
]
}
}
],
"add_note": {
"_type": "link",
"action": "post",
"fields": [
{
"name": "description",
"required": true
}
]
}
}
Document
The Document primitive is represented using an object which includes a key-value pair of "_type": "document".
-
Documents MAY include a
"_meta"key. The value of this SHOULD be an object. If omitted, the default value is treated as an empty Object. -
The
"_meta"object MAY include keys named"url"and"title". -
Any other keys occurring in the Document
"_meta"section SHOULD be ignored by clients. -
The value of the
"url"field SHOULD be a string. This value is treated as relative to the URL of any parent containing document. When a document is loaded from the network then the URL of the top level document is treated as relative to the URL that the content was fetched from. If omitted the default value is treated as the empty string, relative to the URL of the parent containing document or network URL, as above. -
The value of the
"title"field SHOULD be a string. If omitted, the default value is treated as the empty string. -
All other key-value pairs are treated as the document content.
Link
The Link primitive is represented using an object which includes a key-value pair of "_type": "link".
-
Links MAY include keys named
"url","action","transform", and"fields". -
Any other keys occurring in an Link SHOULD be ignored by clients.
-
The value of the
"url"field SHOULD be a string, and is treated as relative to the URL of the parent containing document. If omitted the default value is treated as the empty string, relative to the URL of the parent containing document. -
The value of the
"action"field SHOULD be a string. If omitted value defaults to the empty string. -
The value of the
"transform"field SHOULD be a string. If omitted value defaults to the empty string. -
The value of the
"fields"field SHOULD be a list. If omitted the default value is the empty list.
Link parameters:
-
Each element of the
"fields"list SHOULD be an object. Elements that are not objects are ignored. -
An object item in the
"fields"list SHOULD contain a key"name". The value of this SHOULD be a string. If omitted, the object item is ignored. -
An object item in the
"fields"list MAY include a key"required". The value of this SHOULD be a boolean. If omitted the default value isfalse. -
An object item in the
"fields"list MAY include a key"location". The value of this SHOULD be a string. If omitted the default value is the empty string.
Error
The Error primitive is represented using an object which includes a key-value pair of "_type": "error".
-
Error MAY include a
"_meta"key. The value of this SHOULD be an object. If omitted, the default value is treated as an empty Object. -
The
"_meta"object MAY include a key named"title". -
Any other keys occurring in the Error
"_meta"section SHOULD be ignored by clients. -
The value of the
"title"field SHOULD be a string. If omitted, the default value is treated as the empty string. -
All other key-value pairs are treated as the error content.
-
Errors SHOULD only occur as the top level element. Any Error occurring as a child element inside a Document, Object or Array SHOULD be ignored.
Data primitives
The standard JSON primitives are represented as usual.
- These are Object, Array, String, Integer, Number,
true,falseandnull.
Handling unexpected types
-
Several of the Object structures described above indicate a required type for an element. When the value type is not as expected, the value SHOULD be ignored, and the indicated default value used instead.
-
Any Object with a
"_type"key that is not"document","link"or"error"is invalid. The"_type"key and any"_meta"key are to be removed from the normal parse flow, and the element is to be treated by the client as a standard Object.
Escaping reserved keys
The object keys "_type" and "_meta" are reserved, and should not be included in the standard parsing of key-value contents of Document or Object types.
Core JSON ensures that the reserved "_type" and "_meta" are still valid literal keys, by providing escaping and unescaping rules as detailed below.
Escaping reserved keys during encoding
When any object key matching the regular expression /[\_]+(type|meta)/ is encountered, it MUST be escaped by pre-pending an additional underscore character.
Unescaping reserved keys during decoding
When any object key matching the regular expression /_[\_]+(type|meta)/ is encountered, it MUST be unescaped by removing the leading underscore character.
Canonical style
The following canonical style indicates a set of guidelines that server implementations or client libraries MAY choose to follow, in order to generate a consistent output format for the JSON encoding.
Key ordering
Clients MAY choose to order any Object or Document keys in their output, as follows.
"_type""_meta"(With"url"occurring before"title"in the child Object.)- All keys with a value that is not a Link, ordered alphabetically.
- All keys with a value that is a Link, ordered alphabetically.
Omitting default values
Clients MAY choose to omit any values that are the default when encoding a document.
Using relative links
Clients MAY take advantage of the relative URL transformations made when parsing Documents and Links, in order to encode minimal URL outputs.
- The top level Document MUST include its URL value, without transformation.
- If a child Document or Link has the same scheme, host and port portion as its parent, it MAY omit those portions of the URL, and include only the path, query string and fragment identifier portion of the URL.
- If a child Document or Link has the the same URL as its parent, it may omit the URL entirely.
Indentation and spacing
Client MAY choose to use a concise style as the default. Using this style will ensure that no spacing or indentation is used between tokens.
Clients MAY choose to allow an optional verbose style. Using this style will ensure that ":" delimiters have a following whitespace, "," delimiters have no following whitespace, and elements are newline indented, with four space character indentation level.
HAL
Python implementation: core-api/python-hal-codec
HAL services MUST expose their endpoints with the application/hal+json media type.
Core API documents can be encoded in HAL, with a few limitations:
HAL does not supports parameter or action information on links.
When interacting with a HAL service using Core API, you'll need to explicitly set any actions other than GET. For example, using the command line client:
coreapi action add_note -a post -p description="A new todo note"
Additionally, parameters will not be included in the link descriptions displayed by Core API documents.
Indexing by keys vs indexing by rel values.
HAL uses rel values to identify and index links and embedded documents,
whereas Core API uses the key in the document.
In order to handle this Core API maps between HAL rel values and roughly equivalent key values.
For example, if decoding a HAL document then the link's curie name will be as the key, if it exists.
Valid document structures.
HAL supports documents and links as top level items, where Core API supports documents and links nested anywhere in the parent document.
This introduces some limitations on the valid document structures that Core API can support in HAL representations.
Link help information.
Core API does not yet support help information being associated with links, which HAL provides for.
JSON Hyper-Schema
Python implementation: core-api/python-jsonhyperschema-codec
JSON Hyper-Schema endpoints MUST use the application/schema+json media type.
Core API can support decoding & interacting with JSON HyperaSchema endpoints.
The schema style is less expressive that true hypermedia, as it consists of a single monolithic entry point. Calls to the endpoint typically result in data being returned from the service, rather than a new hypermedia document. Nonetheless, using a Core API client library to interact with a service using its schema definition is far more robust and meaningful than constructing HTTP requests explicitly.
The additional benefit of schemas is that they can be created for existing APIs without any internal changes being required. Furthermore, if clients load the schema definition from disk, then no initial HTTP call to request the entrypoint is required.
OpenAPI / Swagger
Python implementation: core-api/python-openapi-codec
Core API can support decoding & interacting with OpenAPI / Swagger endpoints.
The following constraints currently exist, although future work is planned on each of these:
- Core API does not yet support file upload or download.
- Core API does not yet support encodings other than JSON for request data.
- Core API does not yet support choosing delimiters for lists in query parameters.
- Core API does not yet support help information being associated with links.
HTML
Python implementation: core-api/python-html-codec
Core API also allows servers to respond in a way that allows for direct Web browser based interaction with the API.
By providing an HTML encoding, a service may expose either an API that can be interacted with directly through the browser, or may expose HTML documentation pages, driven by the information in the Core API document model.
Above: An example of an API that can be interacted with in the browser.